Manufacturing Projects for EV Batteries and Semiconductors Catapult Reshoring

A surge in manufacturing projects for EV batteries and semiconductors helped propel reshoring job announcements to the highest number ever recorded. Source: The Reshoring Initiative

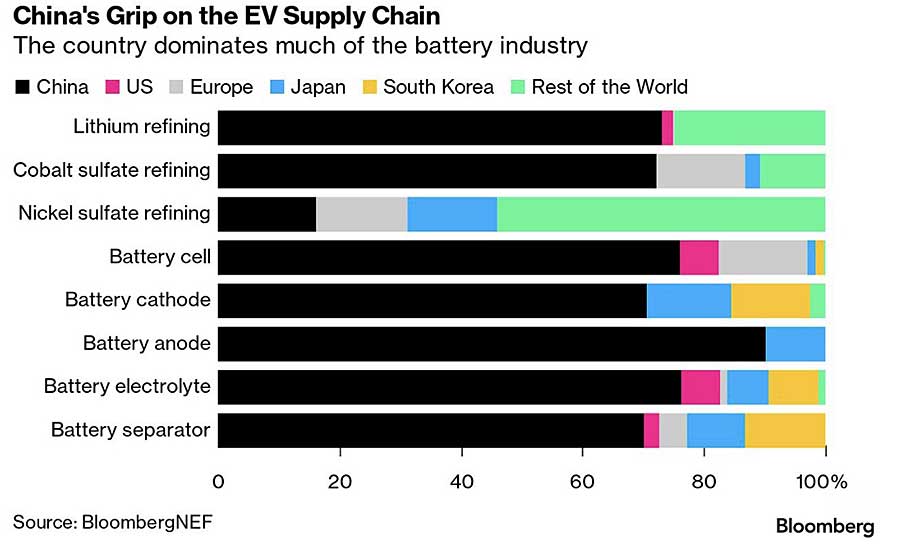
China dominates the global supply chain for lithium-ion batteries, producing 79 percent of the world’s supply in 2021. Source: Bloomberg


Reshoring and foreign direct investment (FDI) created more than 364,000 new U.S. manufacturing jobs in 2022, a 53 percent increase from the 2021. A surge in manufacturing projects for EV batteries and semiconductor chips—combined with the continuing trend of reshoring across a broad range of industries—helped to propel current and future manufacturing jobs to a record high total.
The total number of jobs announced since 2010 is now nearly 1.6 million. New investments in U.S. manufacturing by domestic and foreign companies surged after President Biden’s Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) and Chips and Science Act were passed.
The two acts together inject more than $400 billion into clean energy technology and semiconductor manufacturing via government incentives and subsidies. EV battery and semiconductor investments accounted for more than half of all reshored jobs announced last year.
We expect the federal stimulus to result in further investments in manufacturing capacity for batteries, motors, chargers and EVs. The increased chip investments will also motivate more companies to assemble electronic products here.
In addition, these trends will also increase nearshoring of work from Asia to Mexico, and US manufacturers will need to supply some 40 percent of the value of any parts or products made south of the border. Therefore, we expect 2023 and 2024 to remain strong, continuing at approximately 350,000 announced jobs per year.
U.S.-Made Batteries Are Crucial to EV Transition
Let’s dig deeper into the EV supply chain. Automakers and the U.S. government are spending billions of dollars to establish a domestic battery supply chain. U.S.-made batteries will be critical to manufacturing plans for long-range, zero-emission vehicles. Success in this endeavor will be crucial for our country’s economy, national security, and energy independence.
EV batteries were a major contributor to reshoring in 2022. The electrical equipment industry, which includes battery manufacturing, accounted for 42 percent of reshored jobs in 2022, compared with 4 percent in 2019.
At the moment, China dominates the global supply chain for lithium-ion batteries, producing 79 percent of the world’s supply in 2021. EV battery chemistries depend on five critical minerals whose supply is potentially at risk of disruption: lithium, cobalt, manganese, nickel and graphite. China controls 61 percent of lithium refining for energy storage and EVs, and it controls 100 percent of the graphite processing for battery anodes. The IRA’s rules are broadly aimed at diluting China’s grip over key ingredients for electric motors and batteries.
The U.S. is beginning to ramp up domestic production. Albemarle Corp., one of the largest global lithium producers, recently announced a $1.3 billion investment in a new Mega-Flex lithium processing facility in South Carolina. The plant is expected to support the production of 2.4 million EVs each year.
Chemicals was the third largest industry for reshoring jobs in 2022. This was driven by demand for domestic production of pharmaceuticals, especially vaccines and COVID-19 treatments; renewable fuels, such as hydrogen; and the rare-earth-based chemicals required for batteries.
Government incentives, supply chain interruption risk, and the availability of a skilled workforce were the top reported reasons for reshoring in 2022, accurately reflecting the underlying forces behind the trend. Federal subsidies, part of government incentives, were a new and powerful factor. The IRA will have the largest impact on reshoring and FDI, primarily for production of EVs and EV batteries, both of which were previously heavily dependent on imports from China
Investments in EV plants, battery plants and battery recycling totaling $128 billion have been announced as of December 2022. A greater share of plug-in electric vehicles were assembled domestically than conventional gas-powered vehicles, which means that EVs are already positively affecting the local economy. More than 70 percent of EVs on the road were assembled in North America, and 65 percent were built in the U.S. The latter ratio is expected to reach 80 to 90 percent in the near future. Ford recently announced that some 80 percent of the vehicles it sells in the U.S. are assembled by its 57,000 manufacturing workers in the U.S.
Our 2022 Reshoring Initiative Data Report should motivate companies to further re-evaluate their sourcing and siting decisions by considering all of the cost, risk and strategic impacts flowing from those decisions.
Our main mission is to get companies to do the math correctly using our Total Cost of Ownership Estimator (TCO). By using TCO, companies can better evaluate sourcing, identify alternatives and even make a case when selling against offshore competitors. For help, call me at 847-867-1144 or email me at harry.moser@reshorenow.org.
Looking for a reprint of this article?
From high-res PDFs to custom plaques, order your copy today!